Metal Roof Snow Guards Spacing
Snow Guard Spacing Theory:
Snow and ice can avalanche dangerously off glossy-coated metal roofing. Snow guards are installed to help prevent the dangerous sliding of snow and ice. Our recommended approach to snow retention placement involves positioning the snow guards throughout the entire roof to keep snow and ice from shifting initially. Once frozen precipitation loses its grip on a metal roof and begins a down-hill slide, it is exposed to inertia, and as such, a row of guards or rails placed just along the eave or gutter edge of the roof is not always enough protection against a dangerous roof snow and ice avalanche. If snow and ice are held in place with an effective snow guard layout, the load will be evenly distributed on the roof, and the threat of avalanches can be effectively mitigated. An evenly distributed snow load will also preserve the long-term integrity of the structure and snow guard installation. Snow guards should never be isolated on partial roof sections, such as just over doorways and partial roof sections. Snow guards installed on just partial roof sections may be overloaded since the weight from the unprotected roof area can be easily transferred to the partial areas that have snow retention devices. There are products, however, such as the VentSaver, which is designed to protect roof vents, chimneys, and masts without using snow guards.
Snow guard spacing refers to the distance between individual snow guards or snow retention devices installed on a roof. Snow guards are used to prevent snow and ice from sliding off a roof in large sheets, which can be dangerous to people and property below. Proper snow guard spacing is essential to their effectiveness and the overall safety of the building.
The optimal spacing for snow guards can vary depending on several factors, including:
Roof Pitch
Steeper roofs typically require closer snow guard spacing and multiple rows going up the roof to prevent the sudden release of snow and ice buildup.
Snow Load
The expected amount of snowfall in a region plays a significant role. Areas with heavy snowfall may require closer spacing and multiple patterns of snow guards going up the roof.
Roof Material
The type of roofing material can affect the spacing. Metal roofs, for example, may require closer spacing and more rows than asphalt shingles.
Roof Design
The architectural design of the roof, including valleys, dormers, and other features, can influence snow guard placement.
Local Building Codes
Some areas have building codes or regulations that specify snow guard requirements, including spacing.
Generally, snow guards are spaced evenly across the roof, usually in rows of staggered patterns, to distribute the weight of snow and ice more evenly. Common snow guard spacing ranges from 12 inches to 24 inches apart, staggered horizontally and vertically along and up the roof, although it can be closer or farther apart depending on the factors mentioned above. Consulting with a reputable snow guard company, knowledgeable roofing professional, or engineer is advisable to determine the appropriate snow guard spacing for your specific roof.
A snow guard installation should always be performed by experienced professionals familiar with local building codes and best snow retention practices. Improper spacing and installation can lead to roof damage or failure.
STANDING SEAM ROOF SPACING CHARTS
SCREW DOWN ROOF SPACING CHARTS
OTHER SPACING CHARTS
Snow Guard & Snow Rail Spacing Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Contractors, roofers, and homeowners can all use our intuitive, user-friendly snow guard charts. If you know the pitch of your roof, the distance between your roof panel's seams, your ground snow load, and the type of system that you desire then the challenging portion is already completed. You can access the spacing recommendations for your specific project by selecting the snow retention method that you want. Then select the roof pitch that corresponds to your roof at the top of the chart. For information on your suggested vertical and horizontal spacing, read the description and view the diagram. These charts are only designed for snow loads up to 45 psf. If you have a project in a an area that receives snow load of higher than 45 psf, please fill out the SnoBar/ColorBar Price Quote Form.
Because floating standing seam metal roofing systems often do not allow for roof penetrations, the snow retention system should only be attached with adhesive or clamps. Our standing seam charts can be used on projects with ground snow loads of 45 psf or less. We have options for glue down polycarbonate systems, clamp on SnoBar or ColorBar rail systems, and also individually mounted clamp on SnoCleat Snow Guards for your project. Simply select the product that you are interested in and then pick the corresponding roof pitch to obtain information on proper spacing for your system. Each spacing chart also includes links for the corresponding products. If you have a project in a an area that receives snow load of higher than 45 psf, please fill out the SnoBar/ColorBar Price Quote Form.
Our screw-down charts can be used on projects with ground snow loads of 45 psf. or less. These charts should not be used for standing seam metal roofs. Customers with screw down PBR and R-Panels, can use the Pad Style Glue Down Chart, SnowCatcher Chart, SnoCleat PBR Chart or screw down SnoBar and ColorBar snow rail chart. If you have 2.67 wavy corrugated metal panels, we suggest using the screw down SnoCleat 2.67 Chart or the 2.67 Snow Rail Chart. Each spacing chart also includes links for the corresponding products. Make sure that you are mechanically fastening your snow retention system into purlins, decking, or blocking. Simply select the product that you are interested in and then click on the corresponding roof pitch to obtain information on proper spacing of snow guards for your system. If you have a project in a an area that receives snow load of higher than 45 psf, please fill out the SnoBar/ColorBar Price Quote Form.
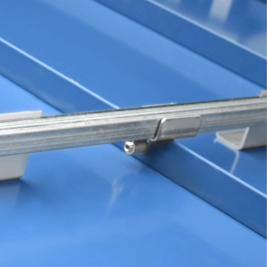
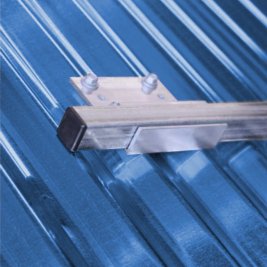
Pad style snow guards are small, individual units that are manufactured from either polycarbonate or metal. These guards can be mounted either mechanically or with adhesive (ONLY when using polycarbonate styles). A snow rail system consists of 6' or 12' long metal bars that attach to your roof with clamps (for use with standing seam roofing) or brackets (for use with screw down roofing). In most cases, a bar system requires less rows of product, but are typically more expensive. Regardless of the system that you select, we never recommend installation in just isolated areas such as above doorways or over HVAC units. A proper system will span the entire length of the roof and will typically require multiple rows up the slope for proper weight distribution.
When working with pad style snow guards, metal and polycarbonate styles are both excellent choices for just about any project with a ground snow load of less than 45 psf. It is critical to make sure that you are obtaining a proper snow guard layout with either type. We offer various options to fit the majority of the roof panels currently on the market. Laboratory Testing showed that in many cases, polycarbonate guards are just as strong, if not stronger than metal guards. Aesthetics are often a consideration for many of our customers when choosing a pad style guard. Most of our Polycarbonate Snow Guards can be either screwed or glued in place and come in a clear finish that is UV stabilized. Additionally, the SnoBlox Deuce comes in a selection of molded Colors. The metal SnowCatcher is made from stainless steel and can be painted, or powder coated to custom match your roof's finish. The PBR SnoCleat is an all-aluminum snow guard that can receive pieces of the roof panel that slide into the front upright and face of the snow guard. Installation of the SnowCatcher and SnoCleat PBR is limited to mechanical mounting only for use on screw down panels.
Our snow guard spacing charts are only recommended for use in areas where the snow load is 45 psf or lower. If you don't know what your snow load is, please consult your local zoning or building permit office. It is always advisable to consult with an architect or engineer prior to ordering. Please complete the SnoBar Price Quote Form or the ColorBar Price Quote Form if your project is in an area with a snow load greater than 45 psf.
Isolated placement installations are never recommended, regardless of the snow retention system that is being used. A layout should be obtained prior to purchasing snow guards. Equal weight distribution of roof snow and ice across the entire structure is a paramount consideration when designing a system for your project. Isolated installations have a high risk of failure, which can cause damage, not only to the snow guards, but also to the roof's panels and structure. This can cause thousands of dollars in damage. It is advised to consult with an architect or engineer before placing an order to ensure adequate snow retention placement.
To have us calculate the number of snow guards necessary for your roof, please fill out the Snow Guards Price Quote form. It will be necessary to know your local ground snow load, roof pitch, panel type, panel valley width and number of panel flats for each roof section to receive an accurate quote.